Gas-jet propelled hemostats for targeted hemostasis in wounds with irregular shape and incompressibility. Journal of Materials Chemistry B 2023, 11(17), 3885-3897.
Published in Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2023
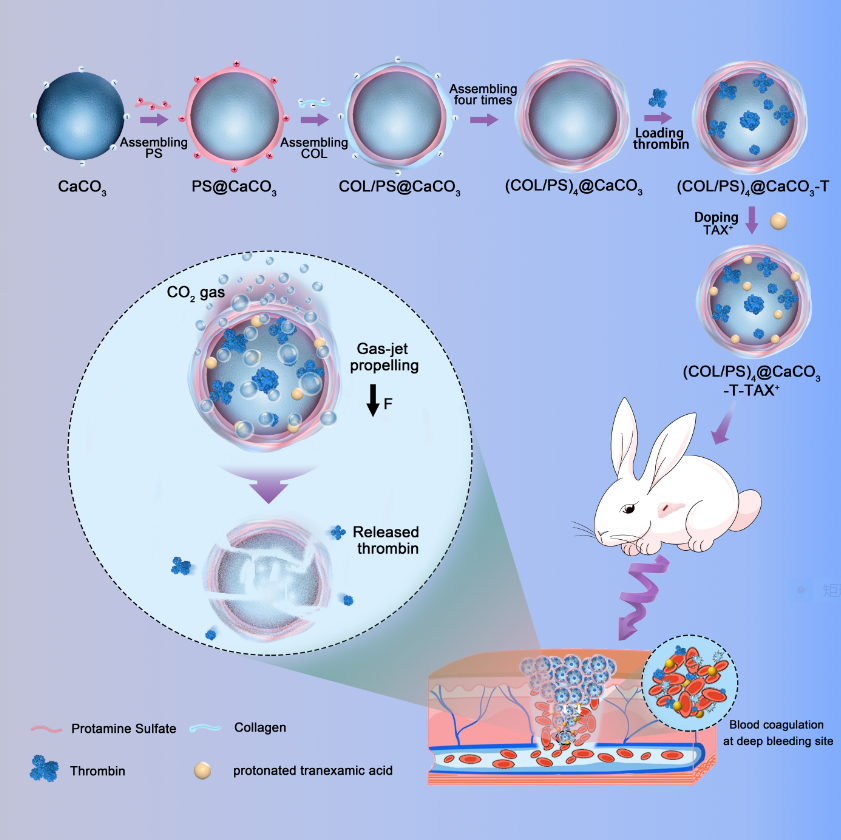
大出血伤口外涌的血流是阻碍止血剂停留在伤口处发挥止血功能的最大阻碍。因此,有效克服血液外涌阻力是止血剂实现快速止血的关键。本研究利用碳酸钙微球与固体酸粉末共混,通过层层组装的方式,制备了一种可以血液响应的“自推进”粉末止血剂。在施加于出血伤口后,可以在血液中自发生成大量微气泡,利用“喷气”作用克服血液外涌阻力而“逆向”递送止血药至隐蔽的出血点,实现止血药在伤口中的“靶向”停留,达到“根部”快速止血的目的。该智能止血粉末不为外力干扰的靶向递送的特性,将为长期困扰的粉体类止血剂无法用于大出血伤口的难题提供全新思路。
Since hemostats are likely to be flushed off a wound by a massive gushing of blood, achieving rapid and effective hemostasis in complex bleeding wounds with powder hemostats continues to be a significant therapeutic challenge. In order to counter the flushing effect of gushing blood, a gas-jet propelled powder hemostat ((COL/PS)4@CaCO3-T-TXA+) has been developed. (COL/PS)4@CaCO3-T-TXA+ dives into the deep bleeding sites of complex wounds for targeted hemostasis. In preparation, protamine sulfate and collagen are first electrostatically deposited on CaCO3, which is then loaded with thrombin, and finally doped with protonated tranexamic acid (TXA-NH3+) to produce the final therapeutic medicine (COL/PS)4@CaCO3-T-TXA+. When applied to bleeding tissues, CaCO3 and TXA-NH3+ from (COL/PS)4@CaCO3-T-TXA+ immediately react with each other in blood to release countless CO2 macro-bubbles, which direct the hemostatic powder, (COL/PS)4@CaCO3-T-TXA+, precisely towards deep bleeding sites from complex wounds. Then the carried thrombin is released to accomplish targeted hemostasis. According to animal studies, (COL/PS)4@CaCO3-T-TXA+ has better effects in rabbit hepatic hemorrhage models; the hemorrhage quickly stops within 30 s, which is roughly 20% less than with the commercial product CeloxTM. The present study provides a new strategy for using powder hemostats to quickly and effectively stop bleeding in complex bleeding wounds.
